Introduction
we’re diving into one of the most intriguing mysteries of the cosmos—black holes, Have you ever wondered if multiple objects can fall into the same black hole? Well, buckle up because we’re going to explore the depths of space to answer this fascinating question.
Black-holes are some of the most enigmatic and extreme objects in the universe. They form when massive stars collapse under their own gravity, creating a point in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. But what happens when more than one object encounters a black-hole? Let’s delve into the science and uncover the mysteries of these cosmic giants.
What is a Black Hole?
To understand if multiple objects can fall into a black hole, we first need to grasp what a black hole is.
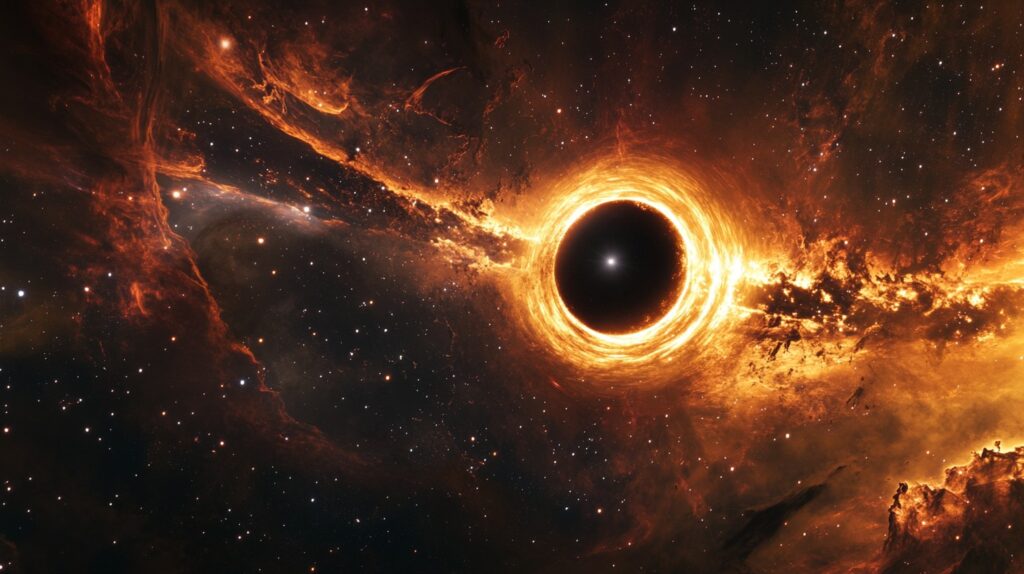
A black-hole is defined by its event horizon, the boundary beyond which nothing can escape its gravitational pull. The event horizon marks the point of no return. Anything that crosses this boundary is inexorably drawn into the black hole.
At the very center of a black hole lies the singularity, a point where gravity is thought to become infinite and space-time curvature becomes infinite. However, the true nature of the singularity remains one of the biggest mysteries in physics.
How Do Objects Interact with Black Holes?
Now that we know what a black-hole is, let’s explore how objects interact with it.
When an object gets close to a black-hole, it’s subjected to intense gravitational forces. If the object is within the black-hole’s gravitational pull, it begins to spiral inward. This process is called “spaghettification” or “tidal stretching,” where the object is stretched and compressed as it approaches the event horizon.
As the object gets closer to the event horizon, it accelerates and heats up, often emitting X-rays and other radiation in the process. This radiation is one of the ways astronomers detect the presence of black holes.
Can Multiple Objects Fall into the Same Black Hole?
so, can multiple objects fall into the same black hole? The answer is yes!
Black holes can, in fact, accumulate matter from various sources. This can happen in a number of ways. For instance, a black-hole in the center of a galaxy can attract and capture stars, gas clouds, and even other black holes.
When multiple objects fall into a black-hole, they are all drawn toward the singularity. Their individual properties—such as mass, spin, and charge—combine, and the black-hole’s characteristics change accordingly. The total mass of the black-hole increases, and its gravitational influence grows stronger.
For instance, if two stars fall into the same black-hole, the black-hole’s mass will be the sum of the masses of the two stars. The black-hole will also retain angular momentum if the stars were rotating. This accumulated matter affects the black hole’s gravitational field and, consequently, its event horizon.
The Fate of Objects in a Black Hole
What happens to objects once they’ve crossed the event horizon?
Objects that fall into a black-hole are believed to be crushed into an infinitely dense point at the singularity. However, due to the extreme conditions, current physics cannot fully describe what happens beyond this point.
Some theories suggest that the information about the objects that fall into a black-hole might not be lost but rather encoded in some way. This leads to the “information paradox,” a topic of ongoing research.
Observing Black Holes and Multiple Objects

Scientists observe black-holes and their interactions with other objects using a variety of techniques.
One of the main methods is through the detection of gravitational waves. When two black-holes merge or when other massive objects fall into a black-hole, they create ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves. Instruments like LIGO and Virgo have detected these waves, providing indirect evidence of such events.
Additionally, telescopes that observe X-rays and other electromagnetic radiation can detect the high-energy interactions of matter falling into black-holes. This helps scientists study the behavior of matter and the characteristics of black-holes.
Theoretical Considerations and Future Research
The study of black-holes and their interactions with multiple objects also involves theoretical physics.
Theoretical physicists use models and simulations to understand the complex dynamics of black-holes. These models help predict how matter behaves when falling into a black-hole and how multiple objects might influence each other in such extreme environments.
Ongoing research and future observations will continue to refine our understanding of black-holes. Upcoming space missions and advanced telescopes will offer new insights into these cosmic giants and their interactions with other objects.
Conclusion
So, there you have it! Multiple objects can indeed fall into the same black-hole, each contributing to the black-hole’s mass and properties. The mysteries of black-holes are far from being fully unraveled, and there’s still so much to learn.

